
1. Because monopolistically competitive firms produce
differentiated products, each firm
a. faces a demand curve that is horizontal.
b. faces a demand curve that is vertical.
c. has no control over product price.
d. has some control over product price.
2. Which of the following conditions distinguishes monopolistic
competition from perfect competition?
a. number of sellers
b. freedom of entry and exit
c. small size firms
d. differentiation of product
3. If existing fast-food firms realize sizable economic profits
in the short run, the demand curves of existing firms will
a. decrease and become more elastic.
b. decrease and become less elastic.
c. increase and become more elastic.
d. increase and become less elastic.
4. When a monopolistically competitive firm raises its price,
a. quantity demanded falls to zero.
b. quantity demanded declines, but not to zero.
c. the market supply curve shifts outward.
d. quantity demanded remains constant.
5. There are several reasons why demand curves may become more
elastic. Among them are
a. the market becomes more monopolistic and cross
elasticities approach zero.
b. the goods become less differentiated and more firms enter
the industry.
c. consumers have fewer substitutes and firms drop out of
the industry.
d. industry demand increases and consumers increase
spending.
6. Which of the following is a characteristic of oligopoly or
monopolistic competition, but not perfect competition?
a. advertising and sales promotion
b. profit maximization according to the MR = MC rule
c. firms being price takers rather than price makers
d. horizontal demand and marginal revenue curves
7. Product differentiation allows the firm to
a. raise price and lower quantity demanded.
b. raise price without suffering a substantial loss of
sales.
c. shift the market demand curve to the left.
d. decrease barriers to entry.
8. The maximum total short run economic profit, or minimum
loss, for the monopolistically competitive firm in this figure is
a. zero.
b. a profit of $575.00.
c. a profit of $2,000.00.
d. a loss of $375.00.
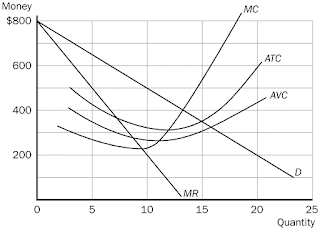
9. The firm in this figure is monopolistically competitive. It
illustrates
a. the shut-down case.
b. a long-run economic profit.
c. a short-run economic profit.
d. a short-run loss.
10. At the profit-maximizing, or loss-minimizing, output level,
the firm in this figure has total costs approximately equal to
a. $2000.
b. $3000.
c. $3600.
d. $800
11. Assume the firm in the figure is currently producing 8
units of output and charging $380. The firm
a. will increase its profits if it raises its price and
reduces its production level.
b. will increase its profits if it lowers its price and
expands its production level.
c. is maximizing profits.
d. will increase its profits if it raises its prices and
expands its production level.
12. Cecilia’s Café is a monopolistic competitor. If Cecilia’s is
currently producing at the output level where her average total cost is
minimized and the café is earning economic profits, then in the long run output
will
a. decrease and average total cost will increase.
b. decrease and average total cost will decrease.
c. remain unchanged as Cecilia’s is doing the best it can.
d. increase and average total costs will decrease.
13. In the long run, freedom of entry into a market forces a
__________ to charge a price equal to average total cost, but average total
cost exceeds its minimum level.
a. perfectly competitive firm
b. monopolistically competitive firm
c. oligopolistic firm
d. pure monopoly
14. Which of the following best describes the idea of excess
capacity in monopolistic competition?
a. Firms produce more output than is socially desirable.
b. The output produced by a typical firm is less than what
would occur at the minimum point on its ATC curve.
c. Due to product differentiation, firms choose output
levels where P > ATC.
d. Firms keep some surplus output on hand in case there is a
shift in the demand for their product.
15. Which of the following individuals quoted below is least
likely to argue that excess capacity in monopolistically competitive industries
is a waste of resources?
a. “An automobile is transportation, nothing else.”
b. “Tomatoes or no tomatoes. The choice of toppings on a
burger can be important to a consumer these days when individualism is
increasingly important to people.”
c. “Gasoline is gasoline no matter what the brand name.”
d. “I take the airline that will get me from A to B at the
lowest price.”
16. The traditional view of monopolistic competition holds that
this type of industrial structure is inefficient because
a. there are too few firms to reach an efficient level of
production.
b. firms do not operate at the output that minimizes average
costs.
c. advertising is not used extensively enough to yield an
efficient differentiation of the products.
d. consumers do not have enough choice among the product
varieties available.
17. Monopolistic competition is considered by some to be
inefficient because
a. price exceeds marginal cost.
b. output exceeds capacity output.
c. long-run profits are positive.
d. All of the above are correct.
18. Perhaps it’s not a problem at all, but if “too much choice”
is a problem for consumers, it would occur in which market structure(s)?
a. perfect competition
b. monopoly
c. monopolistic competition
d. perfect competition and monopolistic competition
19. Which of the following might be an effect of advertising?
a. increased product differentiation
b. increased total costs of production
c. increased demand for the product
d. All of the above are correct.
20. In the long run under monopolistic competition, when firms
advertise,
a. they will still earn zero economic profit.
b. they can earn positive economic profit by increasing
market share.
c. the market price must fall.
d. the market price must rise.
21. Advertising
a. provides information about products, including prices and
seller locations.
b. has been proven to increase competition and reduce prices
compared to markets without advertising.
c. signals quality to consumers, since firms spend so much
money on ads.
d. All of the above are correct.
22. Critics of advertising argue that advertising
a. wastes resources because it creates an image without
necessarily improving product quality.
b. advertising lowers barriers to entry into an industry
because new firms can more easily establish themselves as competitors.
c. advertising increases competition by providing
information about prices.
d. advertising encourages monopolization of markets by
raising entry barriers too high.
23. Many airlines promise “frequent flyer” miles to passengers
who fly their airlines regularly. This is an example of a firm attempting to
create
a. price discrimination.
b. a predatory pricing scheme.
c. discounting below marginal costs.
d. brand loyalty.
24. One of the reasons that Kodak and Fuji films advertise so
much is that
a. each hopes to create a natural monopoly.
b. they are in a perfectly competitive industry where
advertising is the difference between economic and normal profits.
c. they want to develop brand loyalty.
d. they want to increase price elasticities of demand.
25. If some coffee drinkers continue to buy Maxwell House
coffee even when Folger’s coffee is on sale and cheaper, it may be a result of
a. irrational consumer behavior.
b. a high cross elasticity between the two goods.
c. brand loyalty.
d. Maxwell House being a monopoly.
No comments