
1. Which of the
following is an implicit cost?
a. salaries paid to owners who work for the firm
b. interest on money borrowed to finance equipment purchases
c. cash payments for raw materials
d. foregone rent on office space owned and used by the firm
2. Samantha has been
working for a law firm and earning an annual salary of $90,000. She decides to
open her own practice. Her annual expenses will include $15,000 for office
rent, $3,000 for equipment rental, $1,000 for supplies, $1,200 for utilities,
and a $35,000 salary for a secretary/bookkeeper. Samantha will cover her
start-up expenses by cashing in a $20,000 certificate of deposit on which she
was earning annual interest of $1,000. Assuming that there are no additional
expenses, Samantha’s annual implicit costs will equal
a. $55,200.
b. $221,400.
c. $91,000.
d. $146,200.
3. Economists assume
that the goal of the firm is to maximize
a. total revenue.
b. profits.
c. costs.
d. All of the above are correct.
4. The difference
between accounting profit and economic profit relates to
a. the manner in which revenues are defined.
b. how total revenue is calculated.
c. the manner in which costs are defined.
d. the price of the good in the market.
5. In this diagram,
the shift in the total product curve represents an increase in the firm’s
a. costs of production.
b. productivity.
c. diseconomies.
d. market share.
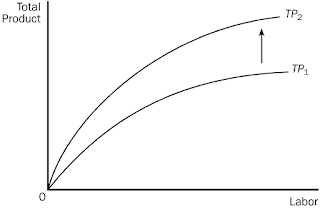
6. Which of the
following could explain why the total product curve shifted in this diagram?
a. A reduction in capital equipment available to the firm.
b. Labor skills have become rusty and outdated in the firm.
c. The firm has developed new technology in their production
facility.
d. The firm is now receiving a higher price for its product.
7. As Al’s Radiator
Co. continues to add workers, while keeping the same amount of machinery, some
workers may be underutilized because they have little work to do while waiting
in line to use the machinery. When this occurs, Al’s Radiator Co. encounters
a. economies of scale.
b. diseconomies of scale.
c. increasing marginal returns.
d. diminishing marginal returns.
8. Which of the
following costs of publishing a book is a fixed cost?
a. author royalties of 5% per book
b. costs of paper and binding
c. shipping and postage
d. composition, typesetting, and jacket design
9. Which of the
following is the best example of a variable cost?
a. monthly payments for hired labor
b. property tax payments
c. monthly rent payments for a warehouse
d. pension payments to retired workers
10. Smith Tire Co.
has total fixed costs of $100,000 per year. The firm’s average variable cost is
$80 for 10,000 tires. At that level of output, the firm’s average total costs
equal
a. $90.
b. $100.
c. $110.
d. $120.
11. Miller
Technologies has average variable costs of $6 and average total costs of $10
when it produces 1,000 units of output. The firm’s total fixed costs equal
a. $2,000.
b. $3,000.
c. $4,000.
d. $5,000.
12. At a firm’s
current output level of 200 units per week, it has 10 employees at a weekly
wage of $500 each. Raw materials, which are ordered and delivered daily, cost
$1,000 per week. The weekly cost of the firm’s capital is $1,250. Which of the
following statements is correct?
Total Variable Cost Total Fixed Cost Total
Cost
a. $5,000 $2,250 $7,250
b. $6,000 $1,250 $7,250
c. $1,250 $6,000 $7,250
d. $2,250 $ 500 $2,750
13. If marginal cost
is greater than average total cost then
a. profits are increasing.
b. economies of scale are becoming greater.
c. average total cost remains constant.
d. average total cost is increasing.
14. The minimum
points of the average variable cost and average total cost curves occur where
a. the marginal cost curve lies below the average variable
cost and average total cost curves.
b. the marginal cost curve intersects those curves.
c. wages are the lowest.
d. the slope of total cost is the smallest.
15. If Franco’s Pizza
Parlor knows that the marginal cost of the 500th pizza is $3.00 and that the
average total cost of making 499 pizzas is $3.30, then
a. average costs are rising at Q = 500.
b. average costs are falling at Q = 500.
c. total costs are falling at Q = 500.
d. average variable costs must be falling.
16. When the marginal
product of labor falls, the marginal cost of output
a. falls, then rises.
b. becomes negative.
c. rises.
d. remains constant.
17. Which of the
following factors is most likely to shift IBM’s total cost and marginal cost
curves downward?
a. a technological advance resulting in increased
productivity
b. higher property taxes charged by the municipal government
c. increased wages to attract additional computer operators
d. a reduction in subsidies from the state government
18. Given the cost
curve described in the diagrams below, the efficient scale of production occurs
at point
a. A.
b. B.
c. C.
d. D.

19. Economies of
scale
a. requires a change in the size of operations and therefore
is a long-run consideration.
b. requires a more intensive use of existing plant and
therefore is a short-run consideration.
c. means that a doubling of plant size will double output.
d. requires a change in the size of plant and therefore is a
short-run consideration.
20. Since the 1980s,
Wal-Mart stores have appeared in almost every community in America. Wal-Mart
buys their goods in large quantities and therefore at cheaper prices. Wal-Mart
also locates its stores where land prices are low, usually outside of the
community business district. Many customers shop at Wal-Mart because of low
prices and free parking. Local retailers, like the neighborhood drug store,
often go out of business because they lose customers. This story demonstrates
that
a. consumers are boycotting local retailers whose prices are
relatively higher.
b. there are diseconomies of scale in retail sales.
c. there are economies of scale in retail sales.
d. there are diminishing returns to producing and selling
retail goods.
21. Some reasons that
firms may experience diseconomies of scale include that
a. the firm is too small to take advantage of
specialization.
b. large management structures may be bureaucratic and
inefficient.
c. if there are too many employees, the work place becomes
crowded and people become less productive.
d. average fixed costs begin to rise again.
22. A local bagel
company plans to keep and maintain its bagel factory, which is estimated to last
25 years. All cost decisions it makes during the 25-year period
a. are short-run decisions.
b. are long-run decisions.
c. involve only maintenance of the factory.
d. are zero, since the cost decisions were made at the
beginning of the business.
23. If a firm
experiences constant returns to scale at all output levels, then its long-run
average total cost curve would
a. slope downward.
b. be horizontal.
c. slope upward.
d. slope downward for low output levels and upward for high
output levels.
24. Which of the
following explains why long-run average cost at first decreases as output
increases?
a. diseconomies of scale
b. less-efficient use of inputs
c. fixed costs becoming spread out over more units of output
d. gains from specialization of inputs
25. The total cost to
the firm of producing zero units of output is
a. zero in both the short run and the long run.
b. its fixed cost in the short run, zero in the long run.
c. its fixed cost in both the short run and the long run.
d. its variable cost in both the short run and the long run.
No comments